Intelligent Production Planning
Comparative Analysis of Traditional and AI-Based Methods for Manufacturing Optimization
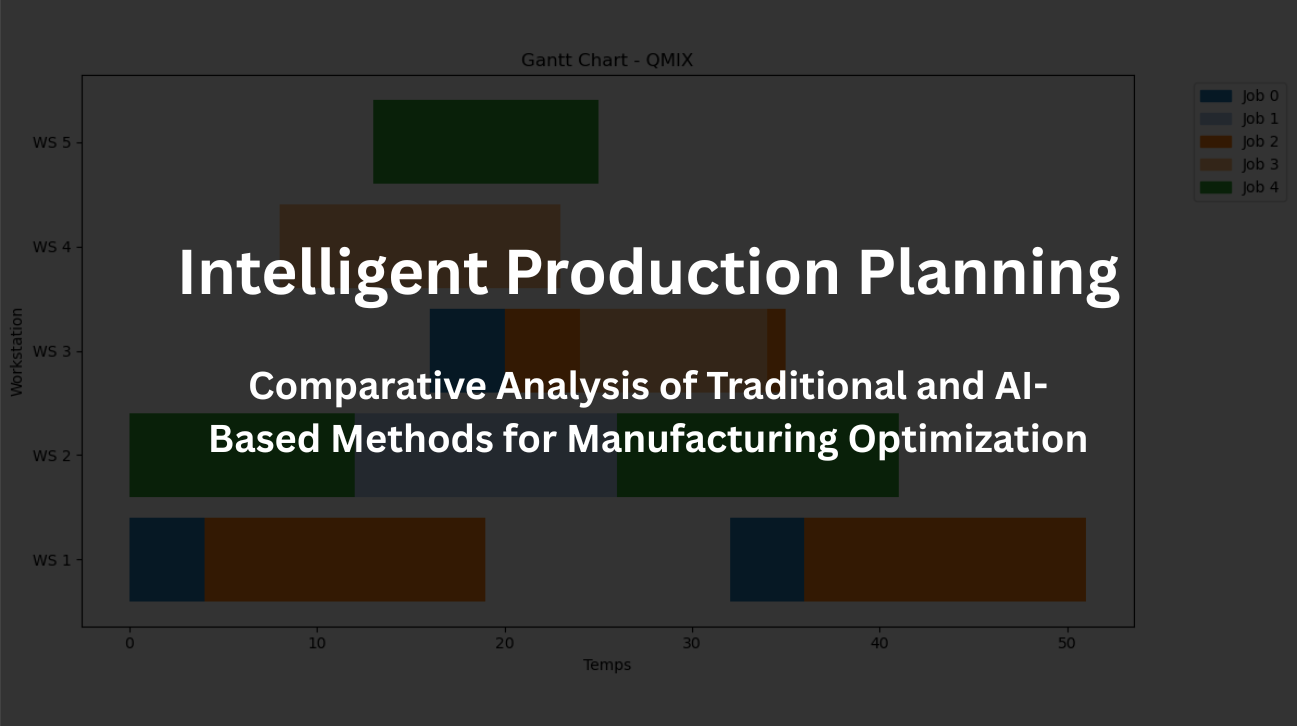
Overview
This project conducts a systematic review and comparative analysis of optimization methods for manufacturing production planning, emphasizing the emergence of AI techniques. It evaluates classical approaches (linear programming, priority rules), metaheuristic algorithms (swarm optimization, genetic algorithms), and machine learning architectures (DQN and QMIX reinforcement learning) in a simulated industrial environment, focusing on minimizing the makespan.
Key Features
- Analysis of classical methods like linear programming and FIFO
- Evaluation of metaheuristics including swarm optimization and genetic algorithms
- Implementation of reinforcement learning with DQN and QMIX
- Simulation of a dynamic manufacturing environment
- Performance comparison based on makespan minimization
Development Process
The project involved designing a simulated Job Shop Scheduling environment with 5 workstations and 5 tasks. Traditional methods (FIFO, Random) and AI-based approaches (DQN, QMIX) were implemented and tested using Python and PyTorch. The methodology included training reinforcement learning models over 500 episodes, optimizing hyperparameters, and evaluating performance against the makespan metric.
Project Details
- Date
- 2025
- Category
- Research
- Team
- Mohamed Boukri
- Client
- École Centrale de Lyon
Technologies Used
Challenges and Solutions
Complexity of the Scheduling Problem
The dynamic environment with multiple jobs, machines, and constraints increased computational complexity.
Solution: Simplified the initial setup with fewer tasks and scaled complexity incrementally during testing.
Training Time for Reinforcement Learning Models
Training DQN and QMIX models required significant time and computational resources.
Solution: Optimized hyperparameters and utilized a replay buffer to enhance training efficiency.
Results and Impact
AI-based methods outperformed traditional approaches, with QMIX reducing the makespan by 25% and DQN by 20.8% compared to FIFO. The study highlights the potential of multi-agent reinforcement learning for agile manufacturing.